Improving operational efficiency is a top priority for manufacturers. There’s a good reason why. Every step in your production process — from initial processing to final assembly — affects output, lead times, and profitability.
You can use that complexity to your advantage. When there are many moving parts, there are plenty of opportunities to make impactful improvements.
This guide outlines how to measure and improve operational efficiency using actionable strategies that will have a real impact on your bottom line.
What is operational efficiency in manufacturing?
Operational efficiency in manufacturing is all about maximizing output while minimizing waste, delays, and unnecessary costs. It reflects how well your production processes convert inputs — like labor, materials, and equipment — into finished products.
Efficient operations help you do more with the same resources. That means shorter lead times, lower operating costs, higher product quality, and better customer satisfaction.
The bigger your manufacturing operations, the more important efficiency becomes. At the same time, efficient processes are easier to scale. That’s why both small job shops and large-scale manufacturers should continuously improve their operational efficiency.
How to calculate manufacturing operational efficiency
There isn’t a single formula that captures “operational efficiency”. Instead, you can measure it by tracking select Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that reflect different aspects of your operation’s health.
Start with the following metrics:
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
OEE is the gold standard for measuring asset performance and a cornerstone of manufacturing efficiency. It tells you what percentage of planned production time is truly productive — and it’s one of the most important indicators of your overall throughput.
Formula: OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
How to calculate the components:
- Availability: Measures downtime losses. Calculated as Run Time ÷ Planned Production Time
- Performance: Measures speed losses. Calculated as (Ideal Cycle Time × Total Count) ÷ Run Time
- Quality: Measures quality losses. Calculated as Good Parts Produced ÷ Total Parts Produced
A world-class OEE score is 85% or higher. To find out where you currently stand, refer to our guide on calculating OEE.
Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency (MCE)
MCE focuses on process efficiency by comparing value-added time to total cycle time. It shows how much of your production time is spent on activities that add value for the customer.
Formula: MCE = Value-Added Production Time ÷ Total Cycle Time
A higher MCE percentage means a leaner, more efficient manufacturing process with less waste.
Labor productivity
Labor productivity measures the raw output of your workforce over a set period. It helps you understand how effectively your team is producing.
Formula: Productivity = Total Units Produced ÷ Total Labor Hours
Track this over time to spot trends and track changes in team performance.
Labor efficiency
Labor efficiency compares how much work was expected to how much was actually done. It’s a quality-focused metric that tells you how your workforce is performing against established benchmarks.
Formula: Labor Efficiency = (Standard Hours for Production × Number of Units Produced) ÷ Actual Hours Worked × 100
An efficiency score over 100% means your team is outperforming the standard. A score under 100% suggests room for improvement.
8 effective ways to improve operational efficiency
Now that we know how to measure it, let’s outline practical strategies your team can implement to achieve operational excellence. The overall theme will be to identify waste, remove friction, and create systems that support consistent, high-quality output.
1. Implement lean manufacturing principles
Lean manufacturing is built on a simple idea: eliminate anything that doesn’t add value. By focusing on waste reduction and continuous improvement, lean practices can make your workflows faster, smoother, and more cost-effective.
A good place to start is by understanding the various types of waste generated in manufacturing, as illustrated in the image below.
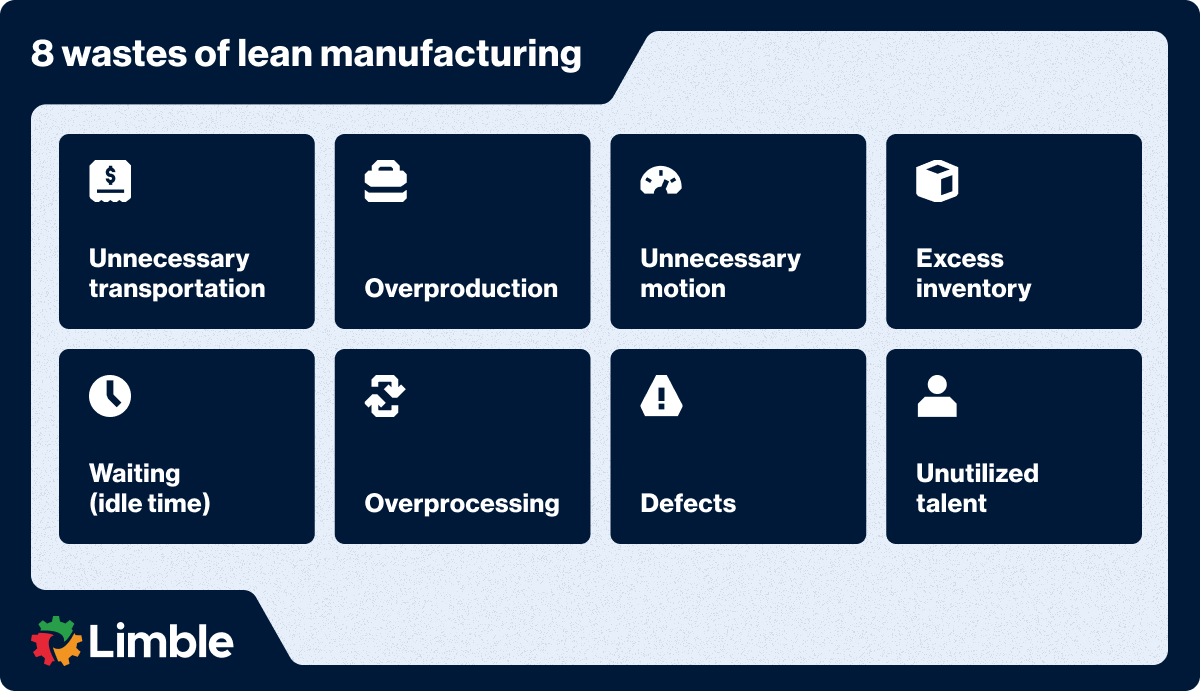
There are many different lean techniques manufacturers can use to boost operational efficiency:
- 5S: A workplace organization method that improves cleanliness, safety, and productivity (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain).
- Value stream mapping: A visual tool that helps you map out the entire production process and identify areas of waste or delay.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) production: A strategy to reduce inventory waste by producing only what’s needed, when it’s needed.
- Kanban: A visual scheduling system that controls the flow of materials and tasks, helping teams limit work-in-progress and avoid bottlenecks.
- Poka-yoke: Error-proofing techniques designed to prevent mistakes before they happen, improving quality and reducing rework.
In the long run, adopting lean principles leads to fewer delays, lower costs, and more predictable production output.
2. Automate repetitive processes
Automation is one of the most effective ways to increase efficiency on the production floor. By automating repetitive, manual tasks, you can reduce labor costs and minimize human error.
Common areas to automate include:
- Material handling: Use conveyors, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), or robotic arms to move parts and materials efficiently between stations.
- Assembly tasks: Automate repetitive jobs like welding, fastening, screwing, or packaging using robotic cells for greater speed and precision.
- Quality control: Use vision systems, barcoding tools, or IoT sensors to automatically inspect and sort products, reducing defects and rework.
- Maintenance scheduling: Implement a CMMS to automate preventive maintenance tasks and automatically generate work orders based on real-time asset condition.
On top of that, you can use technologies like PLCs (programmable logic controllers) and IoT-enabled equipment to get additional process control and visibility. They make it easier to monitor operations and detect problems early.
You don’t need to automate everything at once. Start with high-volume, repetitive tasks that offer quick wins and measurable ROI. Then expand from there.
3. Invest in employee training and engagement
Your equipment is only as effective as the people operating it. Well-trained, engaged employees are essential for creating a safe, efficient, and high-performing production floor.
Here are some ways to strengthen training and engagement:
- Onboarding and continuous education: Ensure every team member understands how to operate machines correctly, follow SOPs, and troubleshoot basic issues.
- Cross-training programs: Teach technicians and operators to perform multiple roles so you can stay flexible during absences, shift changes, or demand spikes.
- Employee engagement initiatives: Involve frontline workers in problem-solving and improvement efforts. They’re closest to the work and often spot inefficiencies leadership doesn’t see.
- Accountability and ownership: Encourage employees to take ownership of their work areas and outcomes. This builds a culture of responsibility and pride.
Investing in your workforce doesn’t just improve skills — it boosts morale and reduces turnover. This benefit should not be underestimated. Quarterly Survey of Plant Capacity Utilization (QSPC) data through Q3 2024 says that approximately 20% of U.S. manufacturers were unable to produce at their full capacity due to labor or skill shortage.
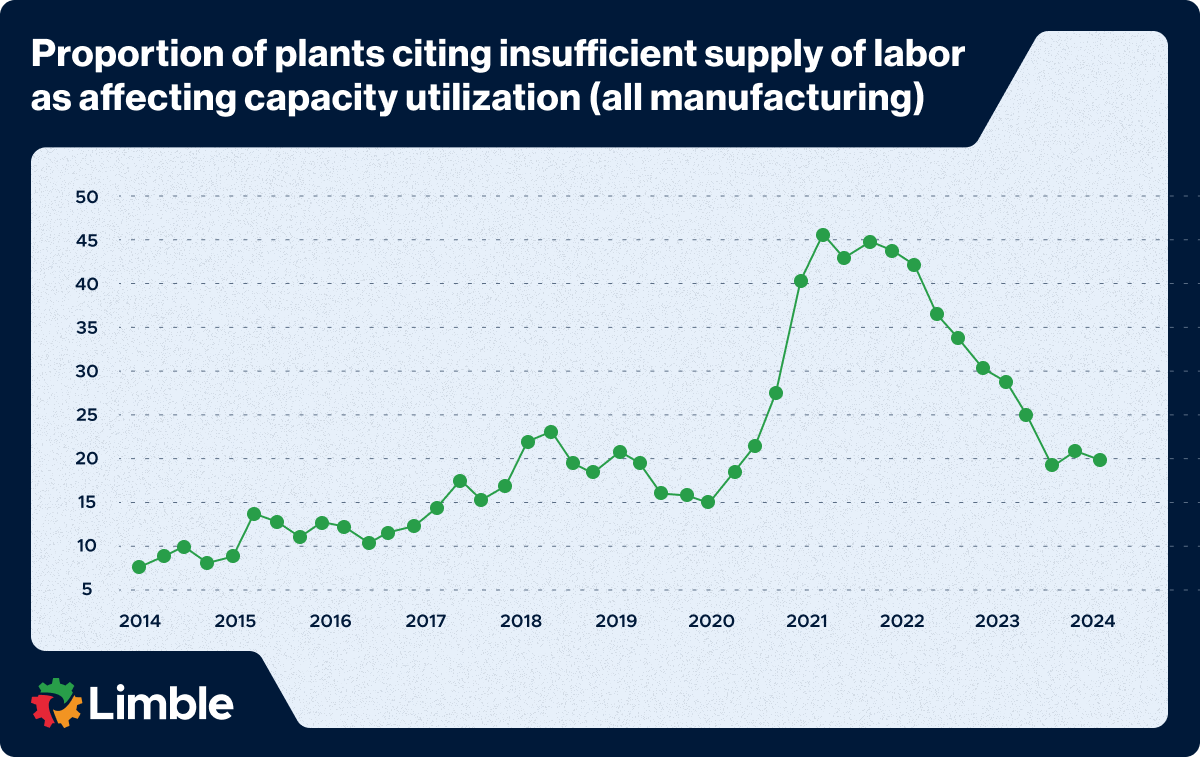
Roughly 1 in 5 U.S. manufacturers can’t reach full capacity due to labor or skills shortages. Source: SCMR
4. Be proactive about maintenance and asset management
Unplanned equipment breakdowns are one of the biggest efficiency killers on the production floor. A proactive maintenance strategy helps you avoid costly downtime, extend asset life, and keep operations running smoothly.
Here’s how to stay ahead of maintenance issues:
- Use preventive maintenance schedules: Instead of waiting for things to break, service equipment on a regular schedule based on usage, time, or its condition.
- Track asset performance over time: Monitor runtime, failure history, and maintenance logs to spot trends and identify underperforming machines.
- Leverage a CMMS: Tools like Limble make it easy to automate work orders, set reminders, and access asset and maintenance data from anywhere.
- Train your team to report early warning signs: Operators are often the first to notice unusual sounds, vibrations, or slowdowns — give them an easy way to escalate issues.
Being proactive leads to more reliable assets. And having reliable assets is a foundation for improving production efficiency.
5. Optimize inventory management
Inventory can either support your production goals — or quietly drain your resources.
Here’s how to tighten up your inventory strategy:
- Use Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory: Reduce waste and free up cash by receiving materials only when they’re needed for production.
- Implement a Kanban system: Use visual signals to trigger restocking only when supplies drop below a certain level.
- Forecast demand accurately: Use historical data and sales trends to better predict what you’ll need and when.
- Increase inventory visibility: Use a CMMS, ERP, or dedicated inventory management software to track product and spare part stock levels in real time across locations.
- Audit regularly: Perform cycle counts and spot checks to keep your records accurate and uncover issues early.
Optimizing inventory means less waste, faster production cycles, and more reliable order fulfillment — all of which directly improve operational efficiency.
6. Standardize workflows
Standardizing workflows is a staple for every efficiency improvement effort. And no wonder. When every worker does a task differently, you get inconsistent results and leave more room for error.
This is why efficient manufacturers:
- Create standard operating procedures (SOPs): Document clear, step-by-step instructions for routine tasks for all frontline teams.
- Use visual aids and checklists: Help workers follow procedures consistently with diagrams, annotated pictures, checklists, or even videos.
- Train to the standard: Make sure all employees are trained the same way, using the same documentation.
- Review and update regularly: As processes improve and you buy new equipment, update your SOPs to reflect current best practices.
Standardized workflows lead to faster onboarding and fewer mistakes across shifts and teams.
7. Use data for continuous improvement
Earlier, we showed you a few different ways to calculate operational efficiency. Those can be combined with additional metrics like cycle time, scrap rate, downtime, and failure metrics to get an even clearer picture of performance.
To build a data-driven improvement process, you’ll have to:
- Implement production management software and a CMMS to accurately calculate and track those metrics.
- Use root cause analysis to dig into the data to find and fix the underlying issues — not just the symptoms.
- Leverage real-time dashboards that provide live data from your machines or systems, helping you react faster and avoid surprises.
- Use structured methods like PDCA or Kaizen to implement and track your continuous improvement efforts.
Data helps move your team from reacting to problems toward preventing them — and continuously getting more efficient.
8. Other practical ways to boost efficiency
There are many small adjustments that can make a big difference in operational efficiency. Here are a few additional strategies worth exploring:
- Review the facility floor layout: Optimize the physical flow of materials, tools, and people to minimize unnecessary movement and delays.
- Rethink scheduling: Adjust shift patterns, production schedules, or staffing levels to better match demand and reduce idle time.
- Implement quick daily stand-up meetings: Brief, focused meetings help teams align on priorities, surface issues, and stay accountable.
- Incentivize efficiency gains: Recognize and reward teams or individuals who contribute measurable improvements to workflows.
- Establish dedicated owners for improvement initiatives: Assign responsibility to specific team members to drive, track, and sustain efficiency projects.
The list doesn’t stop here, but should give you a good idea of what to aim for.
Manufacturing efficiency vs manufacturing productivity
Efficiency and productivity are often used interchangeably — but in manufacturing, they are not exactly the same:
- Manufacturing efficiency is more focused on doing things right. It measures how well you use your resources by minimizing waste, downtime, and unnecessary effort.
- Manufacturing productivity is about doing more with the same input. It focuses on maximizing output.
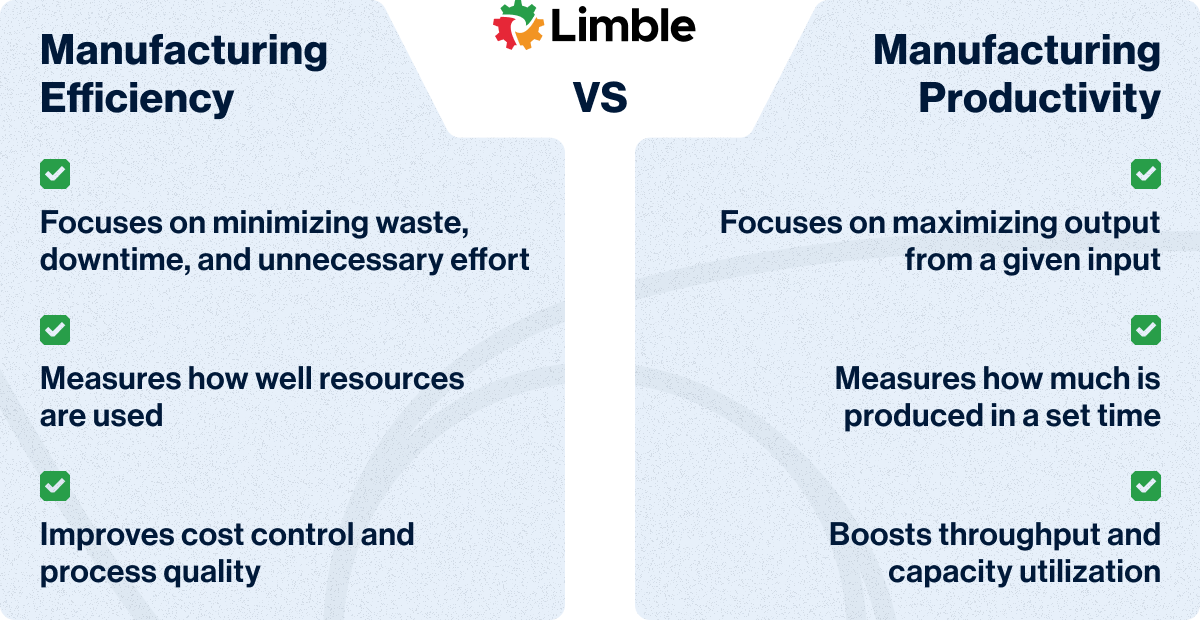
Why does the distinction matter?
Well, you can increase productivity by speeding up production — but if that leads to more scrap, machine breakdowns, or worker fatigue — your efficiency suffers and your operational costs increase. On the flip side, improving efficiency often can reduce waste and lower costs — while the output stays the same.
A quick example:
- A factory that produces 1,000 units in 8 hours with minimal scrap and downtime is both efficient and productive.
- A factory that produces 1,200 units but creates more defects may be more productive, but it is less efficient.
World-class manufacturing operations strive for both — high output and low waste.
Common pitfalls to avoid while trying to increase operational efficiency on your production floor
Efforts to improve operational efficiency in manufacturing can backfire if they’re rushed, poorly implemented, or focused on the wrong things. Watch out for these common mistakes:
- Relying solely on outdated manual processes: Paper logs, whiteboards, and spreadsheets slow you down and increase the risk of errors.
- Focusing only on output (speed), not on process quality: Faster production isn’t helpful if it leads to more rework, waste, or customer complaints.
- Ignoring maintenance or over-maintaining: Skipping preventive maintenance leads to breakdowns, while excessive maintenance wastes time and resources. Use a CMMS to monitor schedule effectiveness and strike the right balance.
- Tracking/measuring performance incorrectly: Inaccurate data and KPI calculation mistakes give you the wrong picture and lead to poor decisions.
- Poor communication between departments and unclear goals: If teams aren’t aligned, you’ll waste time fixing missteps instead of making progress.
Avoiding these pitfalls helps ensure your improvement efforts lead to real, lasting results.
Boost your plant’s efficiency with Limble CMMS
Operational efficiency starts with having the right tools. Limble is a modern, easy-to-use maintenance platform that helps manufacturers optimize all activities tied to maintenance and asset management.
Here’s how Limble helps you put the strategies in this guide into action:
- Automate your proactive maintenance: With Limble, you can set up preventive maintenance schedules based on time, usage, and equipment condition — and even use sensor data to run predictive maintenance.
- Track what matters most: Stop guessing and start making data-driven decisions. Limble’s customizable dashboards let you track key KPIs like OEE, MTTR, and work order completion rates in real time.
- Streamline work and inventory: Equip your team with our top-rated mobile app. Operators get a portal to submit issues quickly. Technicians can receive work orders, follow step-by-step procedures, and manage spare parts inventory directly from the floor.
- Engage your entire workforce: Limble is designed for ease of use, so your team will actually want to use it. This drives adoption, improves communication, and gives you the accurate data needed to fuel continuous improvement cycle.
Let’s back up all that talk with some proof.
Check how Caglia increased labor efficiency by 50% after switching to Limble. This helped them reduce 10‑hour, six‑day workweeks down to a standard 8‑hour, five‑day schedule — without sacrificing output.
Operational efficiency FAQs
What is the single most important metric for a maintenance team to track for efficiency?
While it depends on your specific goals, most manufacturers look at Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) as often the most valuable metric. It combines availability, performance, and quality into a single score, giving you a clear picture of how efficiently your equipment is running.
How does a CMMS like Limble help improve operational efficiency?
A CMMS helps by automating maintenance tasks, centralizing asset data, and improving team communication. With Limble, you can reduce downtime, avoid missed work orders, and make data-driven decisions that lead to faster repairs and better use of available maintenance resources.
Are these efficiency strategies only for large manufacturing corporations?
Not at all. Manufacturers of all sizes can benefit from these strategies. In fact, smaller teams often see faster results because they can implement changes more quickly. Efficiency isn’t about size — it’s about smarter resource utilization.
How long does it take to see results from operational efficiency improvements?
It depends on the strategy, but some improvements—like better scheduling or preventive maintenance — can deliver noticeable results in weeks. Bigger changes like automation or full lean implementation may take longer, but offer larger long-term gains.
What’s the first step to improving efficiency if we’re just getting started?
Start by measuring where you are now. Pick a few key metrics like OEE, downtime, or labor productivity. Then, look for obvious inefficiencies — like frequent breakdowns or excessive inventory — and target those first with simple process improvements.
How do I get buy-in from leadership or other departments?
Use data to make your case. Show how downtime, rework, or delays are impacting output or revenue. When people see the numbers — and that there’s a clear plan to fix the problem — it’s much easier to get support.
How can you maximize operational efficiency in production operations?
Start by identifying and eliminating waste in your processes. Focus on preventive maintenance, employee training, workflow standardization, and real-time data tracking. Use software to streamline maintenance, reduce downtime, and ensure your team has the information they need to work efficiently. Most importantly, treat efficiency as an ongoing effort — not a one-time fix.

