In the past, clouds were in the sky, and the floppy disk reigned supreme. Today, kids see a floppy disk and think we 3D printed the “Save” icon. But we digress.
Today, we access our software via the cloud or on-site servers. Both have their merits and disadvantages regarding how you and your employees access the necessary programs. Which option you choose is based mainly on your company’s unique needs, so let’s look at the two choices.
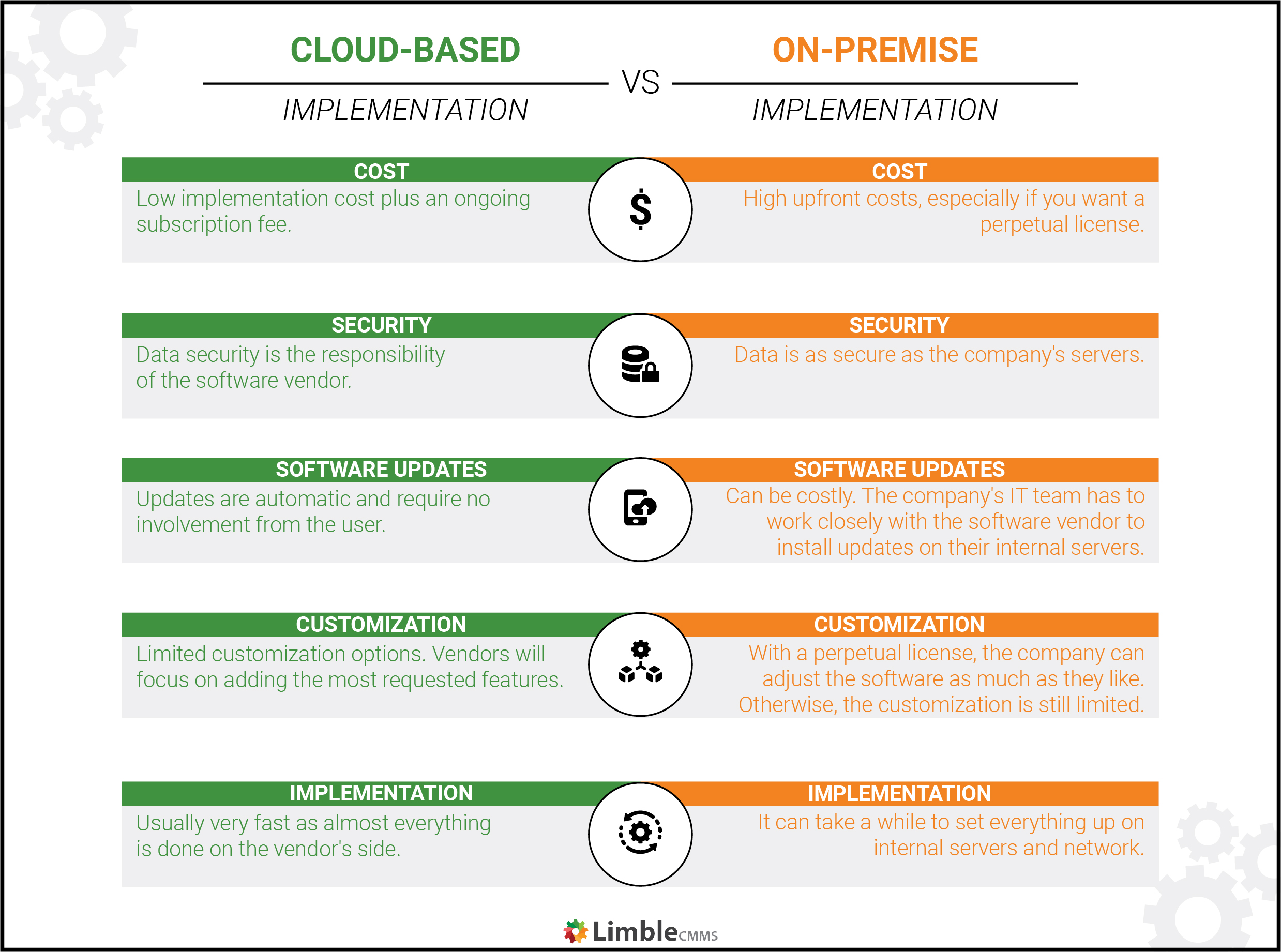
Cloud-based solutions
Cloud-based means all data isn’t stored locally but rather in “the cloud.” Cloud-based solutions are often referred to as SaaS – Software as a Service and are hosted on the vendor’s servers.
You don’t have to physically install anything, and you can immediately access the software through a web browser or a mobile app. Generally, you pay a monthly/yearly subscription to access and use the software.
Benefits of cloud-based solutions:
- Lower startup costs
- You are not involved in the maintenance of the software
- Data security and more regular backups
- It can be adjusted to fit your budget
Disadvantages of cloud-based solutions:
- They can be more expensive
- Potentially impacted by downtime
- Rely and depend on the strength of your company’s internet connection
- May not be secure enough for multi-tenanted environments
On-premise solutions
On-premise software has to be installed locally on the company-owned internal servers. While it can be subscription-based, you’ll usually pay a one-time fee to get a perpetual license to use the software.
There are some considerations for on-premise software. You may want everything stored on-premise if:
- You want to have complete control over your business data and its security
- You already have an on-premise ERP system you want to integrate with
- You plan to buy a perpetual license for the EAM module because you need to heavily modify it to fit your business needs
Benefits of on-premise solutions:
- More customizable: gives you the ability to add in advanced capabilities or features that can support various departments.
- Dedicated IT support on-site: since the software is on-site, you’ll have IT support when you need it.
- Data security: on-site data is less susceptible to cyber threats. Your organization will be responsible for securing its data rather than handing it off to a third party.
- It can be cost-effective over the long term.
Disadvantages of on-premise solutions:
- Longer, more complicated setup and installation
- Not as mobile-friendly as a cloud-based system
- More difficult to move if you need to relocate
- Higher maintenance costs
- Not as easily scaled when your company grows
Hybrid-cloud implementation as a third option
The hybrid-cloud system gives you the best of both worlds. Some data is stored on in-house servers, while your day-to-day information is stored in the cloud for faster access by employees.
Benefits of hybrid-cloud:
- Adaptable: gives your company the agility to change based on their needs
- Better support for a remote workforce: can keep your sensitive data on-premise and other less-critical data on the cloud for employees to access anywhere.
- Reduced costs: easier and less expensive to upgrade/expand as demand spikes.
- Improved business continuity, decreasing downtime: data can be backed up from the servers to the cloud. As demands fluctuate, some can be shifted to the cloud not to overburden the servers.
- Greater control over security: can choose where to house data and workloads based on compliance, policy, or security requirements. The hybrid environment also lets security teams standardize redundant cloud storage, an important aspect of disaster recovery and data insurance.
Disadvantages of hybrid-cloud:
- Hardware costs: building and maintaining your own hybrid infrastructure can be expensive.
- Managing multiple vendors and platforms: managing them over both platforms can be a challenge.
- Less visibility: dividing your computing environments across two or more clouds makes for a complicated operation. This can make it difficult to establish a clear picture of your overall cloud environment, including all the systems, processes, applications, platforms, and requirements you have to manage.