Unscheduled equipment downtime is a nightmare for any industry, increasing costs and reducing productivity. The introduction of predictive maintenance has equipped businesses with a powerful tool to prevent such disruptions.
By harnessing the power of sensors, advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, organizations can predict and prevent equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maximizing productivity.
In this article, we explore 30 different examples of how predictive maintenance is making a significant impact across a variety of sectors.
The role of predictive maintenance in asset management
Predictive maintenance is the monitoring of equipment and assets in real-time to identify signs of wear and tear that could potentially lead to failures. This enables just-in-time maintenance that minimizes downtime and maximizes operational efficiency.
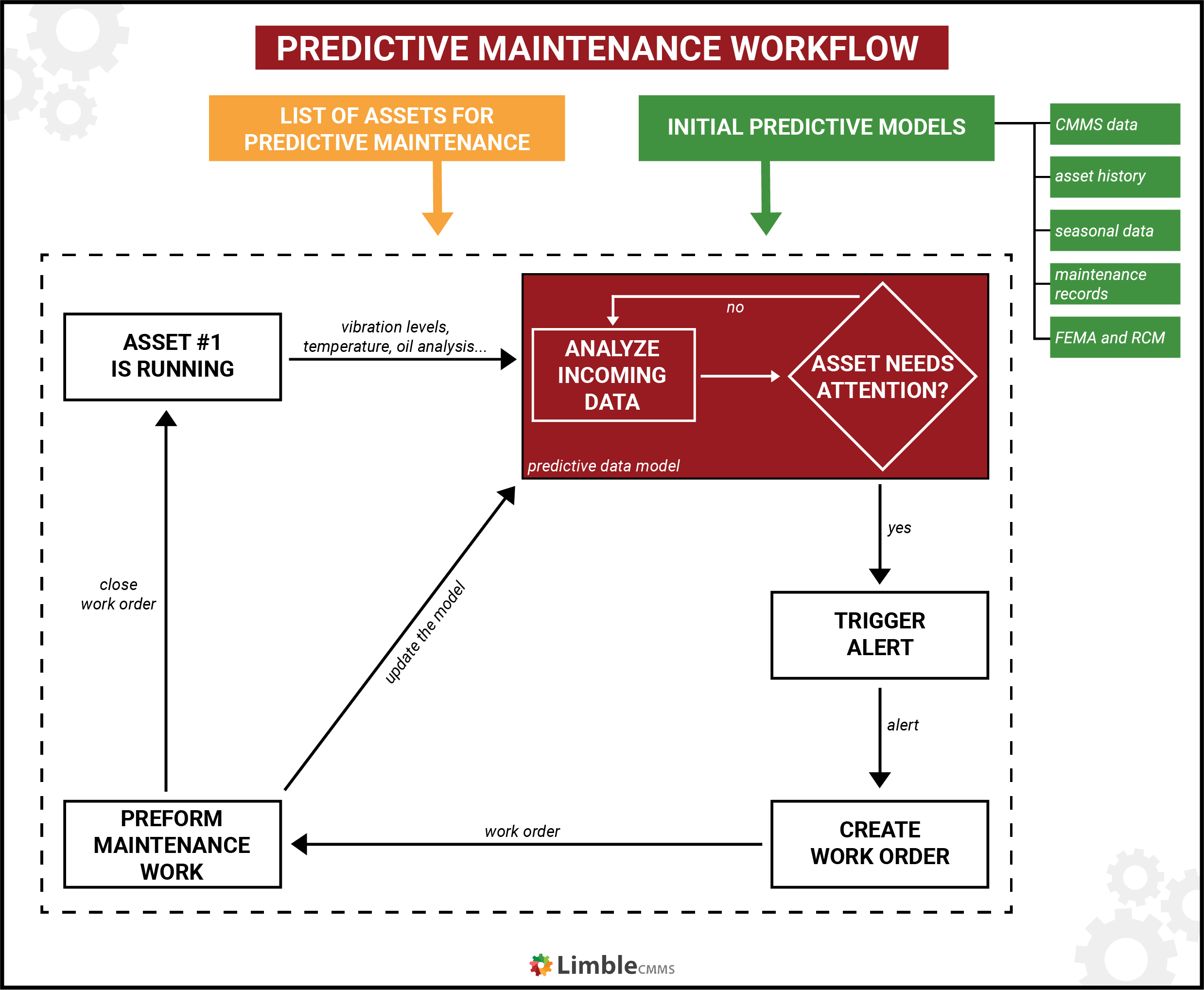
The technological foundation of predictive maintenance is rooted in the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing:
- IoT sensors installed in equipment collect vast amounts of data in real time, monitoring various parameters like temperature, vibration, and pressure.
- This data is then processed and analyzed using AI and machine learning algorithms to detect patterns and anomalies that indicate potential failures.
- Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in the process, facilitating the storage, processing, and analysis of large volumes of data.
Together, these technologies empower businesses with actionable insights to make informed decisions on asset maintenance. This helps them ensure optimal productivity and an extended asset lifespan.
Predictive maintenance examples in manufacturing
Downtime in manufacturing can cause significant financial losses, with interruptions in production, delayed deliveries, and increased maintenance costs. Predictive maintenance helps minimize these losses, allowing manufacturers to monitor the health of critical assets in real time and take proactive action before breakdowns occur.
Here are a few specific examples:
- Vibration monitoring in CNC machines: Utilizing sensors to detect unusual vibrations or sounds that indicate wear and tear, enabling timely maintenance.
- Temperature tracking in motors: Implementing thermal imaging or sensors to monitor the temperature and prevent overheating.
- Oil quality in hydraulic systems: Analyzing oil quality to predict and prevent mechanical failures, ensuring the optimal performance of hydraulic systems.
- Air pressure monitoring in pneumatic systems: Employing sensors to track air pressure levels and predict potential leaks or failures.
- Wear analysis in conveyor belts: Using machine vision or sensors to monitor wear and tear, preventing unexpected breakdowns.
Predictive maintenance examples in the oil and gas industry
The oil and gas industry faces unique challenges when it comes to monitoring and maintaining equipment, particularly in remote and offshore locations. Traditional maintenance approaches that rely on scheduled inspections, can’t offer enough visibility into the real-time condition of critical assets.
Predictive maintenance emerges as a solution to these challenges, enabling precise maintenance interventions based on anomaly detection without compromising performance or safety standards.
Here are some practical examples:
- Compressor monitoring: Employing sensors to track the performance, vibration, and temperature of compressors to prevent failures and optimize efficiency.
- Pipeline integrity: Using ultrasonic sensors or smart pig devices to detect corrosion, cracks, or leaks in pipelines, enabling proactive repairs.
- Drilling equipment health: Implementing sensors to monitor the condition of drill bits, pumps, and other essential drilling equipment, predicting wear and tear.
- Valve and pump performance: Analyzing data from IoT sensors to assess the health and performance of valves and pumps, aiding in timely maintenance.
- Gas leak detection: Using advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms to detect and alert about potential gas leaks before they become an environmental or safety risk.
Predictive maintenance examples in aircraft maintenance
Aircraft maintenance is governed by strict regulations and standards to ensure passenger safety. Traditional maintenance methods that rely on scheduled inspections can sometimes result in either unnecessary inspections or undetected issues that compromise safety and performance.
Predictive maintenance offers a more nuanced approach, leveraging real-time data to provide insights into the actual condition of aircraft components, facilitating timely interventions based on need, rather than a predetermined schedule.
Examples include:
- Engine monitoring: Utilizing sensors to continuously monitor engine performance, detecting anomalies in vibration, temperature, or pressure that could indicate impending failures.
- Landing gear health: Installing sensors in the landing gear assembly to assess the condition of different components and catch wear and tear or other issues as early as possible.
- Avionics systems: Implementing real-time monitoring of avionics systems to identify potential electronic or system failures before they occur.
- Hydraulic systems monitoring: Analyzing data from sensors to maintain the optimal performance of hydraulic systems, predicting and preventing issues like leaks or pressure loss.
- Structural integrity: Using advanced sensors and imaging technology to detect structural issues, such as corrosion or cracks, enabling proactive maintenance.
Predictive maintenance examples in the healthcare industry
In healthcare, equipment reliability is not just about operational efficiency but is intrinsically linked to patient safety and quality of care. Predictive maintenance empowers healthcare organizations to effectively monitor their life-saving equipment and infrastructure, scheduling maintenance based on actual wear and performance data to ensure optimal equipment availability and reliability.
Examples include:
- MRI and CT scanners: Sensors monitor magnet temperature, coolant levels, and calibration status for anomalies like overheating, low coolant, or calibration drift.
- Ventilators: Detection of reduced airflow, pressure anomalies, or clogged filters enables immediate corrective actions, ensuring continuous optimal performance and patient comfort and safety.
- Sterilization equipment: Using sensors to identify issues like temperature deviations or pressure inconsistencies ensures that maintenance occurs before sterilization quality is compromised.
- Infusion pumps: Monitoring mechanical and electronic components to detect anomalies like irregular flow rates or electrical malfunctions ensures precise medication delivery and patient safety.
- Diagnostic Equipment: Employing sensors to track the performance of equipment like EKG and ultrasound machines, identifying issues such as signal interference or image clarity degradation.
Predictive maintenance examples in the energy sector
The energy sector plays a crucial role in powering our modern world. Equipment efficiency and reliability in this sector directly impact the delivery of energy to millions of homes and businesses. With the escalating demands for energy, downtime or equipment failure leads to significant service interruptions and financial losses.
Examples include:
- Transformer monitoring: The health of transformers is tracked by monitoring oil quality, temperature, and electrical currents. Anomalies like oil degradation or current fluctuations are identified for timely maintenance, averting failures and outages.
- Generator performance: By using real-time sensors to monitor vibration, temperature, and electrical output, businesses can pinpoint issues like overheating or electrical imbalances to optimize generator performance and longevity.
- Grid systems: Implementing advanced monitoring technologies to detect fluctuations or imbalances in the grid enables immediate interventions that uphold grid stability and prevent blackouts.
- Nuclear reactor health: Advanced sensors continuously monitor radiation levels, temperature, and pressure, identifying irregularities and ensuring that the reactor operates safely and efficiently.
- Battery storage systems: Sensors track temperature, charge cycles, and voltage, finding anomalies that trigger maintenance activities — ensuring optimized battery performance and reliable energy storage.
Predictive maintenance examples in real estate and facilities management
In the real estate and facilities management sector, optimum performance and longevity of building systems and equipment is paramount to providing safe and comfortable spaces for occupants. Unexpected equipment failures can lead to costly repairs, decreased property value, and dissatisfied occupants.
Examples include:
- HVAC systems: Sensors monitor temperature, airflow, and humidity levels, identifying irregularities like unexpected temperature fluctuations or reduced airflow, and facilitating preemptive maintenance to ensure comfort and air quality.
- Elevator and escalator performance: Utilizing sensors to track mechanical performance and wear, pinpointing issues like motor strain or misalignment.
- Security systems: Implementing real-time monitoring to assess the operational integrity of alarms, cameras, and sensors, identifying failures or vulnerabilities.
- Plumbing systems: Employing sensors and analytics to monitor pressure and flow rates, detecting leaks or blockages early to prevent water damage and maintain system efficiency.
- Electrical systems: Utilizing sensors to monitor load, voltage, and current, catching unusual fluctuations or overloads to ensure safety and system reliability.
Use Limble CMMS to run your predictive maintenance programs
Implementing and running predictive maintenance is so much easier when you have the right software support.
With built-in PdM templates, seamless preconfigured sensor integration, and a partnership with the global leader in industrial data analytics and visualization, Limble CMMS offers you a plug-and-play package for starting your own predictive maintenance program.
If you’re seriously considering investing in predictive maintenance, this is a great place to start. Reach out to our team to learn more.
