Machine Uptime
Everything you ever needed to know about machine uptime.
What is machine uptime?
Machine uptime is defined as the time a piece of machinery was available and operational in a given time period.
It gives us a sense of how reliable a machine is — a high machine uptime indicates high machine reliability and vice versa.
How to calculate machine uptime?
The opposite concept of machine uptime is machine downtime.
When you have the numbers for one of those metrics, calculating the other one is trivial. You just need to subtract the figure from 100.
The equation to calculate machine uptime is as follows:

Machine downtime is easier to observe and record. Due to this fact, the common methodology is to calculate machine downtime and subtract it from 100 to get the figure for machine uptime.
Machine Downtime = (Number of seconds machine was down / Total number of seconds observed) *100
Machine Uptime = 100 – Machine Downtime
Example of a machine uptime calculation
You are observing one of the conveyors in your facility. If the machine was down for 30 minutes in a window of 12 hours you were observing, you can calculate its uptime by inserting the figures into the equation above.
Machine Downtime = (30*60)/(12*60*60) *100 = 4.17%
Machine Uptime = 100 – 4.17 = 95.83%
Therefore, in our example, the observed conveyor had the uptime of nearly 96%.
Checklist for Creating a Preventive Maintenance Plan
Following a consistent Preventive Maintenance Plan can make life easier. Use this checklist to create your own!

Example of low equipment uptime
In order to avoid production interruptions, your machines have to be available and operational throughout the production cycle.
The production consists of multiple processes done in a sequence. When a machine experiences unplanned downtime, the processes that are upstream and downstream from the failed machine are affected.
Let’s say a production process involves five steps in this sequence:
- Cutting
- Machining
- Joining
- Polishing
- Quality check
The machine required for the joining phase of the production is experiencing failure. The polishing and quality check stations remain idle because they can perform their tasks only on the materials that have gone through the joining process.
On the other hand, the cutting and machining stations are still operational, so the inventory gets piled up.
The failed joining machine caused a bottleneck and a delay in the production process. The result — a capital and operational efficiency loss.
Benefits of high equipment uptime
As reference in the example from the last section, high machine uptime leads to:
- More reliable and predictable production schedule
- Improved productivity
- Reduced unscheduled downtime
- Lower cost of operation
- Lower maintenance workload and costs
Remember, reliable machines ensure your production processes run smoothly and without significant delays.
Five proven ways to maximize machine uptime
There are various reasons for regular equipment failures in production facilities — poor maintenance, operator error, equipment or tool failure, etc.
In order to maintain stable production, you have to find ways to increase uptime for critical equipment. Here are some ideas to get you started.
1. Choose your machines and parts wisely
When procuring machines for your production facility, machine uptime has to be a major factor to take into consideration. In other words, choose your OEMs and vendors wisely.
When making purchasing decisions, opt for high-quality machines from reputed vendors.
Let’s say you need to drive a conveyor in your factory. You can pick between a magnetic drive and a drum motor. Both will accomplish the same purpose, but drum motors experience far more maintenance issues compared to magnetic drives.
These are the kind of choices you’ll have to make in order to maximize the uptime of your machine. The same decision process applies to procuring spare parts.
2. Implement condition monitoring and predictive maintenance
Condition monitoring is employed to supervise the operating characteristics of a machine. It can help you determine if a machine is working as expected.
Modern machines used in production are Internet-enabled, which allows you to measure, collect and record sensor data in a digital format.
If a machine is not working in the ideal state, the sensor data makes it much easier to identify the root cause of the problem, and forecast a potential machine failure in the future.
Condition monitoring and predictive maintenance are maintenance strategies that help reduce the rates of unexpected machine breakdowns, helping you achieve higher machine uptime.
3. Use Problem-Failure-Action (PFA) codes
Despite the extreme care you take, every machine will eventually fail. At that point, you’ll need to take reactive maintenance actions to bring it back online.
PFA codes are short hands to easily identify the problem, failure, and action to be taken:
- Problem codes indicate the problem faced by the machine.
- Failure codes determine how the problem has manifested.
- Action codes determine the maintenance action that needs to be performed.
When you use automation with strong protocols for PFA codes, the problem and failure code automatically provide the action code corresponding to it.
Let’s assume we have a problem code P112 which indicates overheating. Failure code (F213) determines the problem has manifested because of coolant leakage. Automatically, the action code (A134) dictates the need of sealing the coolant chamber (maintenance action).
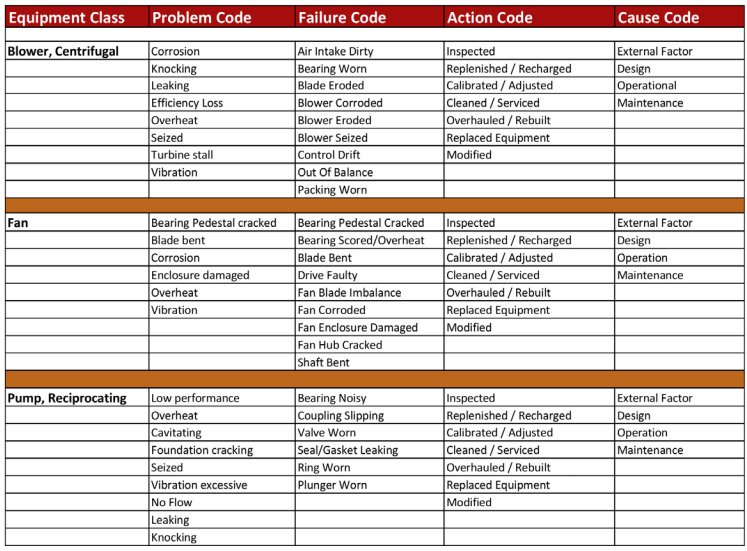
An example of reliability codes for a blower, fan, and pump. Source: Swain Smith
PFA codes are just one of the ways to reduce the mean time to repair (MTTR) and increase equipment uptime. Other options you should take into account are:
- Proper training of your maintenance technicians
- Creation of standard operating procedures (SOPs)
- Optimization of spare parts and inventory management process so maintenance actions do not get delayed due to lack of inventory
4. Equipment redundancy
Equipment redundancy is a reliability engineering methodology that improves machine availability and reliability.
Imagine a scenario where two identical machines perform the same process simultaneously. When one of the machines fails, the other is ready to take over the entire load.
The aim of equipment redundancy is not to increase the uptime of each machine, but to increase the uptime of the entire system/production process.
5. Utilize a CMMS
A maintenance program is an important factor in keeping a high machine uptime.
Manually coordinating and managing all the maintenance activities in a facility, in real-time, is nearly impossible. However, with a modern CMMS system, it becomes perfectly doable.
With CMMS you can:
- Create, assign, and track maintenance work orders
- Provide storage and access to maintenance manuals, checklists, and standard operating procedures (SOP)
- Store all maintenance and machine data for reference and analysis
- Track and store condition-monitoring data
- Create and track KPIs and a maintenance schedule for all equipment
- Perform predictive maintenance
In other words, CMMS makes sure that all maintenance processes that impact machine uptime are finished on time, and up to the required standard.
High uptime = good time
High machine uptime helps you squeeze the maximum out of your production assets. It delivers high operational efficiency and lower running cost.
Operations managers have to take every measure possible to ensure high machine uptime. Cloud-based CMMS solutions like Limble let you keep a handle on all aspects of machine maintenance, and are a must-have solution for every production plant.
If you’re looking for ways to improve machine uptime and reliability, give Limble CMMS a try. For more info, you can contact us via email, request a free demo, or start a free trial.
FAQ
Why use CMMS software to track maintenance metrics?
Using CMMS software simplifies tracking complex maintenance metrics, fosters data-driven decisions, enhancing efficiency, reducing downtime, and aiding in regulatory compliance all in one.
Is Limble Mobile CMMS app user friendly?
Limble is consistently rated Easiest-to-Use CMMS on review sites like G2, Capterra, and Software Advice. And our customers agree. With our mobile CMMS app, teams experience 30%+ better productivity, on average, requiring little to no training or ramp-up time. Our CMMS app can travel with your team, no matter where they go! Visit our App Store or Google Play for more information.
Can I connect to other systems?
Limble provides seamless, pre-built CMMS Integrations with the most widely used software systems. That means no help from a developer or your IT team is required. Learn more about our integrations.
How secure is the Limble CMMS platform?
At Limble, our world-class data security practices ensure your account information is safe. We use state-of-the-art technologies and industry best practices to maintain a secure infrastructure, including SOC-II Type II certification, regular penetration testing, and continuous security training for our staff.


