Prescriptive Maintenance (RxM)
Everything you ever needed to know about prescriptive maintenance.
What is prescriptive maintenance (RxM)?
Prescriptive maintenance (RxM) is a proactive maintenance strategy that uses machine data to determine and recommend needed maintenance on equipment. Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) performs in-depth analyses of a machine’s condition and provides maintenance recommendations for increasing longevity and reducing failure.
Table of Contents
- Everything you ever needed to know about prescriptive maintenance.
- What is prescriptive maintenance (RxM)?
- How prescriptive maintenance compares to similar maintenance strategies
- How prescriptive maintenance works
- When to use prescriptive maintenance
- Precise maintenance for broad applications
- Related Content
The benefits of prescriptive maintenance
Investing in a prescriptive maintenance strategy comes with many benefits that contribute to a business’s success. Some of these benefits include:
- Better equipment reliability: By predicting failures and offering precise tasks to reduce the risk of that specific failure, RxM improves the reliability of each asset.
- Improved equipment longevity: When equipment fails less and receives scheduled proactive maintenance, its lifespan is extended.
- Increased employee safety: Prescriptive maintenance helps identify and address potential safety risks before they escalate. Regular inspections and maintenance can mitigate safety hazards, protecting both equipment and personnel.
- Cost savings: Proactive and precise maintenance is more cost-effective by targeting high risk potential failures and avoiding unnecessary maintenance or expensive repairs and downtime.
- Optimized maintenance scheduling: Prescriptive maintenance enables organizations to schedule maintenance actions more efficiently by using data to accurately forecast the best planned maintenance windows, minimizing disruption to operations.
- Adherence to compliance and regulations: RxM helps organizations meet strict regulations by ensuring the equipment is safe and well-maintained in accordance with standards.
- Competitive advantage: Organizations that use prescriptive maintenance can gain a competitive edge as a result of the additional efficiency and precision in their maintenance practices.
Examples of prescriptive maintenance
Prescriptive maintenance is not a new concept. Companies worldwide use this strategy to achieve greater operational efficiency. Here are a few examples:
Airplane Maintenance
Boeing, an aircraft manufacturing company, offers data analytics services to its clients. Their Boeing Analytx team has used data analysis to diagnose early failure modes in the Boeing 787 hydraulic spoiler power control unit (PCU).
The PCU has two internal motor windings whose dual failure signals an alert on the flight deck and grounds the aircraft until replacements are sourced and installed.
Elevator Maintenance
The German multinational conglomerate ThyssenKrupp utilizes prescriptive analytics in its elevator servicing operation. Data from its elevator network is used to identify tasks critical to the safe and reliable operation of the elevators. It can predict five days in advance when an elevator will shut down due to door problems, automatically scheduling a technician and assigning the four most likely actions that could resolve the pending issue.
Such accuracy prevents outages with passengers onboard and allows technicians to fix the problem with 90% accuracy.
Pump Maintenance
A multinational mining company uses prescriptive analytics on the circuits most critical to their metal-refining process. The system provides specific pump repair instructions 40 days prior to a predicted pump failure.
How prescriptive maintenance compares to similar maintenance strategies
Prescriptive maintenance enhances a well-rounded maintenance management strategy. It takes the entire maintenance program to the next level by using data to shorten troubleshooting and recovery time by providing recommendations for optimal asset performance.
These recommendations can be carried over to other parts of the maintenance strategy, like incorporating them into a preventive maintenance schedule.
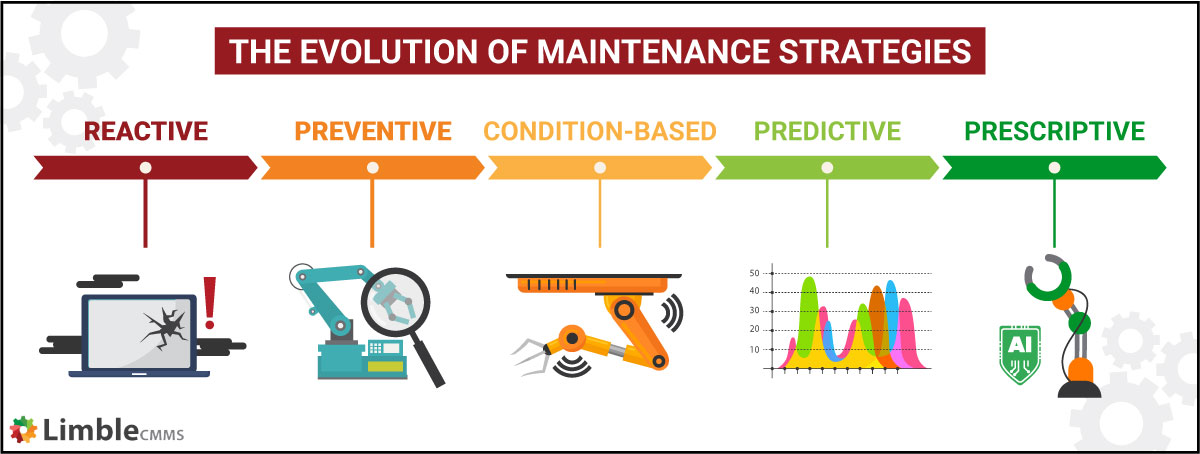
Prescriptive maintenance versus predictive maintenance
Prescriptive maintenance (RxM) and predictive maintenance (PdM) are very similar. Predictive maintenance uses data and analytics to predict when equipment is likely to fail. It uses sensors and monitors to collect real-time data, which is analyzed to identify patterns that could indicate potential problems.
Prescriptive maintenance takes PdM a step further by not only predicting failure but providing recommended actions to prevent those failures..
Prescriptive maintenance versus reliability-centered maintenance
Reliability-centered maintenance (RCM) is a broader maintenance strategy that identifies the most effective maintenance approach for each component of a system. It helps organizations create a cost-effective strategy that aligns with a system’s reliability requirements.
Prescriptive maintenance may be a component of a comprehensive RCM plan by offering specific instructions for each component based on the data it collects. The real-time data from prescriptive maintenance enhances RCM with a more tailored approach for components where sufficient data is available.
How prescriptive maintenance works
Technology and data analytics play a huge role in how prescriptive maintenance works. It requires a lot of data from each piece of equipment – historical data, error codes, service data, and more. This data allows machine learning programs and AI to create prescriptive algorithms that predict equipment failure and provide recommendations for failure prevention.
Sensors connected to the equipment, paired with software programs, collect real-time data. Either hard-wired or via wifi, signals about equipment’s operating conditions pass through a network where sophisticated monitoring software captures, aggregates, and analyzes the data.
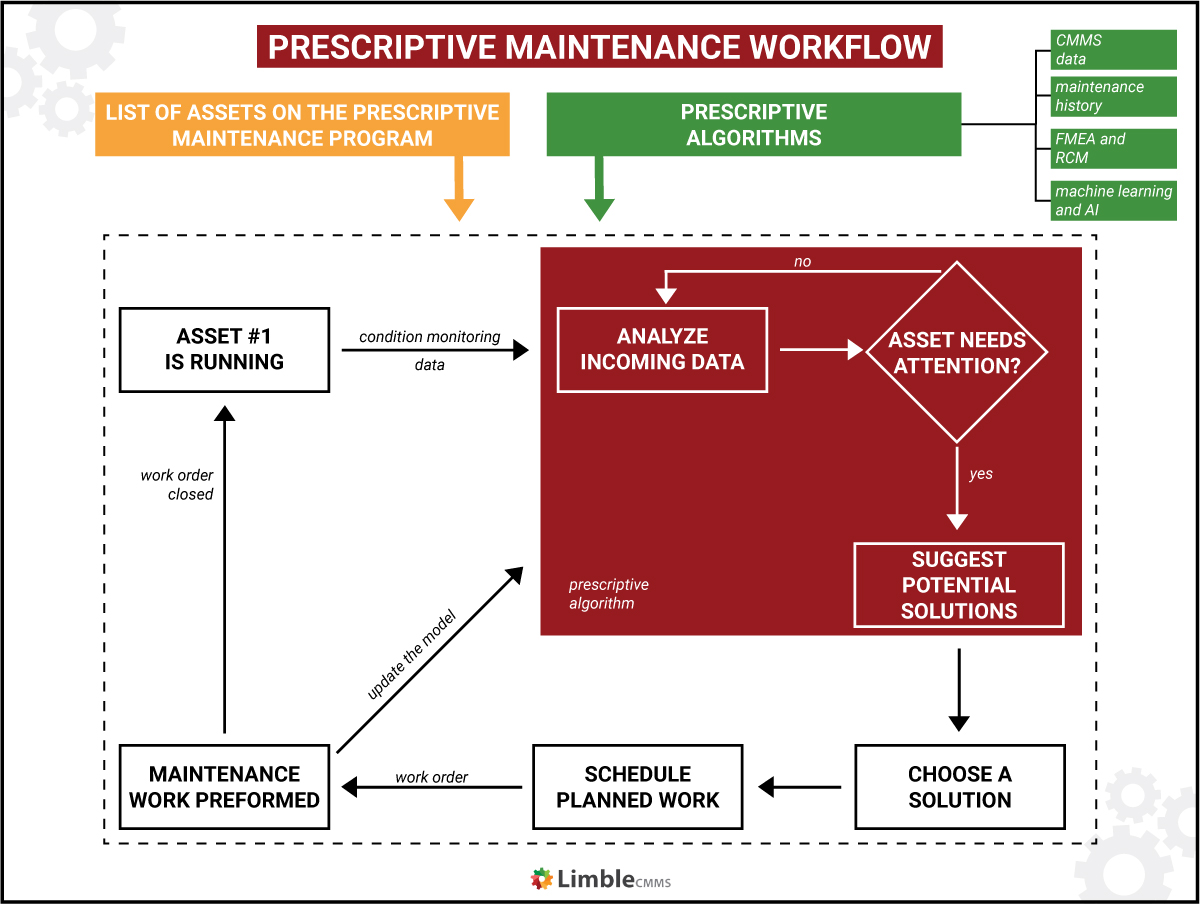
For a simple explanation, prescriptive maintenance works via the following steps:
- An asset, armed with condition monitoring sensors, sends data to its paired software.
- The software analyzes the data to look for signs of potential failure and provides a set of solutions based on historical maintenance.
- Some software systems can automatically schedule the task in the maintenance calendar.
- Maintenance professionals review task recommendations, chooses a solution, and performs the maintenance work.
- Once the maintenance work is performed, information is fed back into the software to enhance predictions and recommendations.
Tools and requirements for a successful prescriptive maintenance program
To implement a successful prescriptive maintenance program, an organization must be equipped with a variety of tools:
- Data collection and monitoring tools: Reliable data collection is a necessity for receiving accurate predictions from prescriptive algorithms.
- IOT (Internet of Things) connectivity: IOT devices (sensors, equipment, and central monitoring system) must have secure and reliable connectivity.
- Maintenance management software: Software like a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) has the capability to connect to sensors, store and analyze data, run prescriptive algorithms, and enable automation of maintenance task scheduling.
- Communication and reporting tools: Access to reports and quick communication with team members and the prescriptive maintenance software (like a CMMS) allow organizations to quickly respond to new RxM recommendations.
- Cybersecurity tools: Any organization that operates in IOT needs a robust cybersecurity system to ensure the security of collected data and communication channels.
When to use prescriptive maintenance
Any company that relies on machinery to operate at peak performance can benefit from prescriptive maintenance. Here are several examples of industries that utilize prescriptive maintenance, and why:
- Manufacturing: Plants with complex production lines and machines can use RxM to prevent equipment breakdowns and minimize unplanned downtime.
- Energy: Power plants use RxM to optimize the performance of equipment like turbines and generators to maximize energy output and reduce disruptions.
- Healthcare: Medical equipment, like MRI machines and other diagnostic tools, retain optimal performance and have minimized risk of unexpected failures with the help of RxM.
- Transportation: Transportation, shipping, and logistics companies use RxM to reduce delays and maintain adherence to strict operating schedules.
- Oil and gas: Equipment like pumps, compressors, and drilling machinery require reliability in order to operate safely and efficiently.
- Telecommunications: Organizations in this sector use RxM to optimize the performance of network infrastructure, reduce service outages, and ensure seamless communications.
- Aerospace and defense: In this sector, RxM can proactively identify and resolve issues in aircrafts, missiles, and other critical systems.
Want to see Limble in action? Get started for free today!
Precise maintenance for broad applications
Prescriptive maintenance plays a large role in the effective operation of many industries.
The journey starts by using smart maintenance, implementing a CMMS solution, and expanding preventive maintenance capabilities. Organizations build upon that by installing condition-monitoring sensors on problematic assets. After some time, they have enough historical data to bring in a data scientist to develop predictive models.
It all starts by implementing a modern, powerful, cloud-based CMMS solution. Kick off your journey today by requesting a demo or starting a free trial of Limble CMMS.


