Heating and cooling are basic processes that are required in virtually every industry. This is why industrial boilers and chillers have seen widespread adoption across many different sectors.
As an important part of smooth day-to-day operation of your facility, it is paramount to understand what chiller maintenance includes and how to keep chillers in good operating condition through proactive maintenance.
The purpose and importance of industrial chillers
Industrial chillers play a key role in setting up a temperature-controlled environment. Just as a boiler heats fluid in its chamber, chillers remove heat from fluids. The cooled fluid is circulated through a heat exchanger to cool equipment or parts of the process stream.
Industrial chillers have 3 broad use cases:
- Air conditioning: Water mixed with ethylene glycol is used as a coolant for air conditioning purposes. The chilled coolant is distributed to heat exchangers to cool spaces in buildings.
- Controlled cooling: Chillers are used for controlled cooling in various industrial processes. They are used in:
- Injection and blow molding
- Chemical processing
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Printing press
- Plastic industry
- Power generation stations
- Food processing units
- Die-casting and machine tooling
- Welding process
- Rubber manufacturing
- Laser applications
- Semiconductor manufacturing
- Dehumidification: Cooling condenses the moisture in the air. Air can be effectively dehumidified with industrial chillers.
There are many industrial processes where maintaining specific environmental conditions is essential.
For example, pharmaceutical production often happens in air-conditioned environments. Production carried out without adequate air-conditioning will be defective and can even harm lives. Having a reliable air-conditioning system is critical.
Chillers are also used in processes that require controlled cooling. A great example is injection molding. Molten plastic is poured into molds to form plastics of different shapes. Chillers help maintain the right temperature to hold the shape. If the chiller breaks down, the complete injection molding process has to be halted.
Types of industrial chillers
There are many ways to categorize industrial chillers. Based on the basic working principle, chillers can be classified as:
- Vapor compression chiller: A mechanical compressor powered by electricity, steam, or a turbine. It is used to compress coolant in vapor form.
- Vapor absorption chillers: These types of chillers use heat that is generated as waste in other industrial processes for the thermodynamic process to chill the coolant.
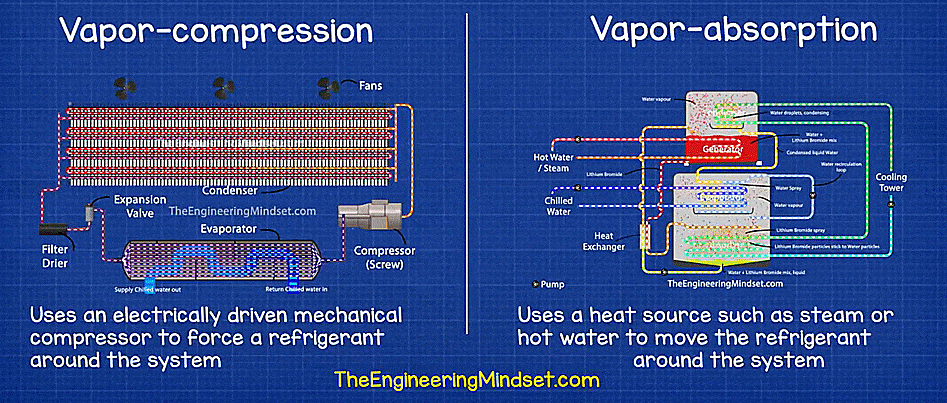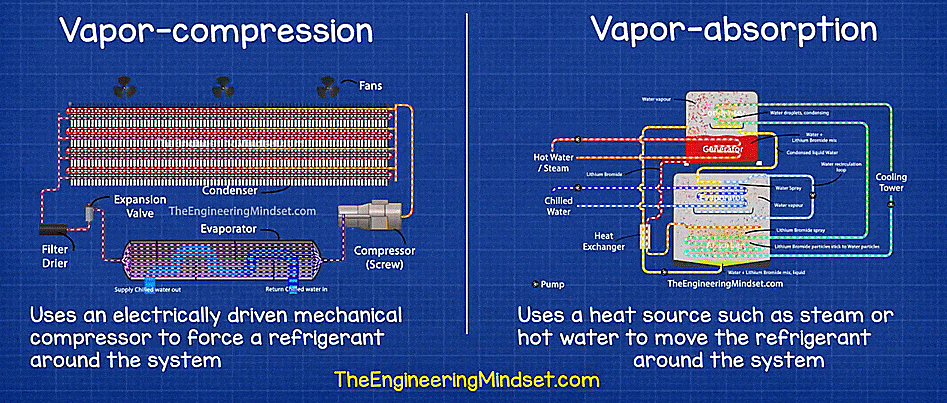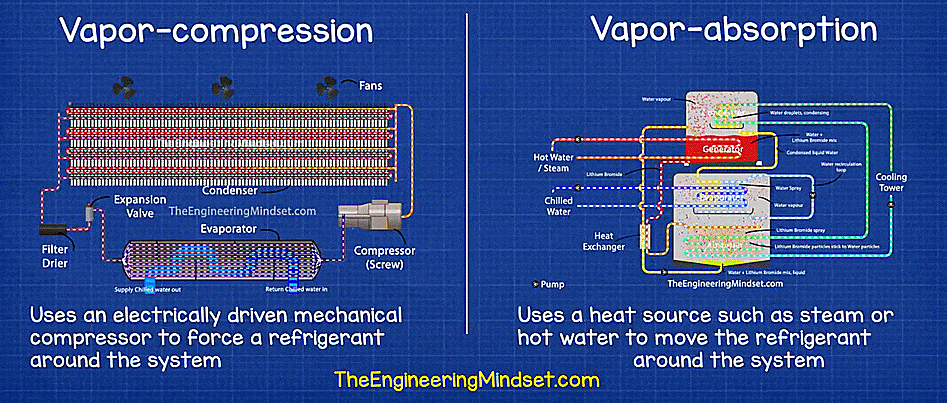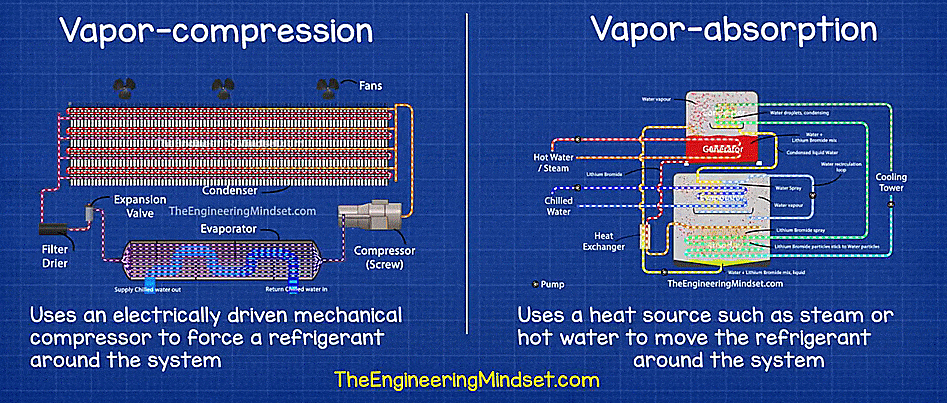
Vapor compression vs Vapor absorption chiller. Source: The Engineering Mindset
Based on how the heat is removed, vapor compression chillers can be classified into:
- Air chillers: As the name indicates, air is used to remove heat. Additional fans are set up to expel heat. Air chillers are easy to install, but they consume more energy in comparison to water chillers.
- Water chillers: Heat is removed by pumping water to the cooling tower. The high heat capacity of water makes it an energy efficient chiller.

Air cooled and water cooled industrial chillers. Source: HVACWAVETECH
Chiller maintenance is intricately connected with how chillers work. Each type of industrial chiller has its nooks and crannies you will need to watch out for.
When creating a preventive maintenance plan for any asset, we always recommend you combine personal experience with OEM-provided guidelines, and take the operating conditions of your facility into consideration.
This should be enough to build a decent initial plan. If you use maintenance software, you can also pull historical maintenance information before assigning frequencies to specific maintenance tasks.
Checklist for Creating a Preventive Maintenance Plan
Following a consistent Preventive Maintenance Plan can make life easier. Use this checklist to create your own!

Chiller maintenance checklists
Routine maintenance of industrial chillers is required to maintain high uptime and extend the useful life of the asset. A nice bonus is that well-maintained chillers have a reduced power consumption.
Below, we outline daily, weekly, monthly, and annual maintenance steps you should consider to keep industrial chillers in good operating condition at all times.
Daily chiller maintenance checklist
Daily tasks to be performed involve checking the chiller’s regular operation:
- Check the temperature of chilled water entering and leaving the chiller system.
- Check and verify the temperature of condenser water entering and leaving the system.
- Check the power and current drawn by the compressor.
- Check sump oil level and temperature.
- Check condenser and evaporator pressure.
- Inspect and record oil pressure readings.
- Check for any abnormal noise and vibration from the chiller system.
Weekly chiller maintenance checklist
Some of the weekly maintenance tasks to be performed are:
- Check the sump oil level and top-up if required.
- Check the liquid level using site glass.
- Inspect pipes and coils for visible leakages.
- Check the exterior condition of the condenser.
- Observe chiller operation for unusual sounds or vibration.
- Check and record all operating temperatures and pressures. Ensure that all the numbers match normal operating conditions.
Monthly chiller maintenance checklist
Common monthly maintenance tasks to be performed on your chillers include:
- Check components for wear and tear.
- Check the level of lubrication in the centrifugal pumps and motors. Top up the lubrication if required.
- Check the condenser and clean the coils.
- Clean condenser water strainers.
- Run the chiller on full load and check the liquid level in the evaporator.
- Inspect the compressor motor for operational temperature. Ensure motors are not overheating.
Annual chiller maintenance checklist
In addition to daily, weekly, and monthly maintenance checks, you should schedule planned downtime to:
- Chemically wash condenser coils.
- Change all oil filters.
- Change all oil. Make sure to use only approved oil.
- Straighten fins and fans of air-cooled condensers.
- Check the liquid line filter. If required, change it.
- Check the health of water strainers. If needed, replace them.
- Check the quality of circulating water for water-cooled condensers. Change the water if required.
- Inspect the health of isolating valves. Lubricate the moving parts of the isolating valve.
- Inspect and verify the operation of the valve limit switch.
- Inspect and verify the operation of the vane damper.
- Inspect the physical condition of the starter panel.
- Check the contactors and tips of electrical components.
- Check the condition of terminal lugs. Replace them as needed.
- Inspect loose connections in electrical circuitry and its components.
Best practices for maintaining industrial chillers
Over the years, maintenance professionals have tried and tested various approaches to chiller maintenance. Here are some best practices recommended by the industry:
- Cleanliness: Keep the chiller and its surrounding environment clean. This helps to reduce inefficiency and improve overall performance.
- SOPs and checklists: Create standard operating procedures (SOP) for all chiller maintenance activities. Create preventive maintenance checklists out of the SOPs. Use them to ensure that maintenance tasks are performed up to the required standard.
- Maintenance records: Keep record of all maintenance activities and measurements (such as temperature and pressure readings). You can use cloud platforms like CMMS to store that data in an easily accessible place.
- Preventive schedules: Create preventive schedules for chiller maintenance. The schedule created has to be in alignment with OEM recommendations and inputs from experienced technicians. You can use a CMMS like Limble to automate and organize maintenance work and stay on top of your spare parts inventory.
- Treated water: Regular water causes corrosion. Use treated water to reduce the chances and impacts of corrosion, as well as to reduce scale formation inside conduits.
- Oil testing: Regularly test the quality of oil and lubricants used in chillers via spectrometric analysis. Replace the oil as soon as degradation in oil quality is detected.
Keep in mind that these are just rough recommendations. You will have to adjust maintenance frequency based on the age/condition of your asset, operating conditions, and the type of chillers you run.
Keeping your industrial equipment in check
Industrial chillers are critical components in industrial operations. The maintenance of industrial chillers has to be done diligently, adhering to industry conventions. If possible, you should use a CMMS system to manage all industrial maintenance activities, chiller maintenance included.
If you want to learn more about Limble CMMS, do not hesitate to request a demo, contact us, or start a free trial.

This was an extensive explanation of PM and planned maintenance. Its an eye openner, wish to learn more. Thanks.