Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance programs use technology to predict when equipment breakdowns will occur and prevent them.
An essential component of Industry 4.0, predictive maintenance strategies involve the use of condition-monitoring tools to proactively plan and schedule repairs and equipment replacement. Implemented effectively, predictive maintenance helps lower operational costs, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of critical assets.
What is predictive maintenance (PdM)?
Predictive maintenance is an advanced type of condition-based maintenance that has emerged thanks to the emergence of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors for monitoring the performance and condition of assets. Real-time data collection and analysis helps maintenance departments diagnose defects and predict breakdowns to ensure they schedule repairs in a timely manner.
Table of Contents
- Predictive maintenance programs use technology to predict when equipment breakdowns will occur and prevent them.
- How does predictive maintenance work?
- Predictive maintenance challenges
- Benefits of predictive maintenance
- Predictive maintenance: industry use cases
- Getting started with predictive maintenance
- What’s next for predictive maintenance?
- FAQ
- Related Content
Preventive maintenance management and predictive maintenance management
Preventive maintenance (PM) describes a number of different approaches to managing assets and preventing equipment failures. At its most basic, preventive maintenance involves planning and scheduling maintenance work proactively in an attempt to stop breakdowns and other issues from occurring in the first place. It’s the opposite of reactive maintenance, which involves servicing assets only after they’ve experienced breakdowns.
When is predictive maintenance useful?
Despite its many potential benefits, predictive maintenance is not always the most cost effective approach for every piece of equipment. For some pieces of equipment, the cost of completing repairs would exceed the cost of replacement. In these instances, a purely reactive approach may be your best choice. Predictive maintenance activities are most effective for high-cost, high-criticality assets whose typical failure modes are easily identified with monitoring systems.
How does predictive maintenance work?
Managing a predictive maintenance program takes more than just technology. An effective program also depends on a well-trained staff, clear processes, and an internal culture capable of promoting continuous improvement.
Here’s a closer look at some of what goes into an effective predictive maintenance program.
Predictive maintenance software
Predictive maintenance software track real-time health and performance data for assets. Numerous components come together to make these solutions useful for predicting and preventing breakdowns.
Condition-monitoring sensors
Organizations can install a variety of different sensors directly onto assets. These track asset performance in real time by measuring factors like temperature, pressure, and vibrations. Sensors offer an accurate assessment of asset health without disrupting performance or impacting productivity.
IoT Technology
All that data won’t do you any good if you stop at the collection stage. Internet of Things (IoT) technology connects your sensors to other platforms and distributes data across your systems for analysis.
Predictive data models and algorithms
All that sensor data helps to develop the predictive algorithms that power PdM programs. The more data your algorithms absorb, the more accurately they’ll predict machine failures. You can get started by building predictive models with the help of historical data and maintenance logs. As sensors collect more and more data, you’ll get a baseline for improving accuracy over. You’ll ultimately gain an automated system capable of monitoring operating conditions in real time, predicting failures based on data anomalies, and sending out alerts when assets deviate from established performance standards.
Predictive maintenance techniques
Predictive maintenance tools use a range of techniques to assess the health of critical assets and help teams make data-driven decisions. Here are a few of the most common condition-monitoring techniques that support predictive maintenance systems.
- Infrared thermography: One of the most versatile techniques for monitoring asset condition, infrared thermography involves the use of specialized cameras to detect dangerously high temperatures within pieces of equipment.
- Ultrasonic acoustic monitoring: Most business assets emit some type of sound during normal operations. Subtle nuances in these sounds could signify trouble. Though the human ear alone could miss the sounds that suggest excess wear tear, acoustic monitoring equipment can detect them and send alerts.
- Vibration analysis: Used for high-speed rotating equipment, vibration analysis The technique helps to identify potential sources of disruption like imbalances, misalignment, and excess wear and tear. The dependable method is considered especially cost effective for manufacturing organizations.
- Lubrication and oil analysis: A non-invasive method, this type of analysis involves the use of oil and lubricant samples to assess wear and tear on machinery.
Predictive maintenance workflow
In predictive maintenance programs, algorithms analyze performance and historical data. When an asset requires proactive maintenance, predictive maintenance solutions automatically trigger an alert. Then, the appropriate individuals create and assign work orders.
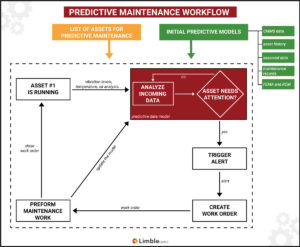
Here’s a look at how maintenance departments manage and improve their predictive maintenance programs.
Predictive maintenance challenges
Why doesn’t every organization implement predictive maintenance strategies? Because it’s not as simple as checking a box. Maintenance teams often run into challenges as they introduce and refine their new programs.
- Up-front costs: It’s not cheap to implement the cutting edge solutions behind predictive maintenance. Many organizations rely on other types of maintenance simply because they can’t afford to embrace new tools.
- Complexity: Not every organization can handle all the complexities of implementing preventive maintenance technology. Make sure you’re ready to integrate disparate solutions and manage huge quantities of data.
- Training needs: To get the most from new solutions and processes, you’ll need to take the time to carefully introduce changes to your team.
The organizations who have successfully implemented predictive maintenance are those who have taken care to prioritize the right equipment and map out a strategic program.
Benefits of predictive maintenance
Predictive strategies allow for more precise planning and maintenance scheduling than other types of preventive maintenance.
- Reduced maintenance costs: Scheduling maintenance activities with the help of predictive analytics allows you to allocate maintenance resources more efficiently. With time, you’ll realize cost savings by reducing overtime and improving spare parts inventory management.
- Minimized equipment downtime: Completing maintenance tasks at the exact right moment helps to avoid unplanned breakdowns, maximizing the uptime and productivity of your assets.
- Improved asset performance and extended asset lifecycles: When you stop minor issues from evolving into major problems, your machines will experience less wear and tear and remain operational for longer.
- Increased productivity and safety: Unexpected breakdowns leave you dealing with extra downtime as teams perform corrective maintenance. Post-breakdown chaos could pose injury risks for your operators and technicians. With a more informed approach to maintenance, you’ll see improvements to key metrics like Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time to Repair (MTTR).
- Better relationships with customers and suppliers: The efficiency and productivity boosts enabled by predictive maintenance can have an impact across your whole supply chain. Suppliers and customers alike will appreciate doing business with a data-driven organization whose ordering and output are always predictable.
Predictive maintenance: industry use cases
A report by McKinsey Global Institute projects that connecting physical assets to IoT solutions could generate up to $11 trillion annually in economic value by the year 2025. Organizations are expected to adopt PdM at a greater rate as the financial and operational cost of the necessary technology continues to drop.
Here are a few industries that are currently at the forefront of predictive maintenance implementation.
PdM in the manufacturing industry
Manufacturers are taking note of the benefits of PdM. McKinsey also predicts that manufacturers may save between $240 billion and $630 billion by the year 2025 thanks to predictive maintenance.
The everyday applications of predictive maintenance in manufacturing are numerous.
- Using vibration sensors to identify patterns of fragile spindles in milling machines
- Measuring the temperature differential upstream and downstream of the heat exchanger to identify early signs of clogging
- Monitoring robot CPU and housing temperatures
PdM in the transportation industry
Connected transportation devices are also on the rise. PdM use among fleet managers has resulted in a measurable decrease in on-road breakdowns and mechanic diagnostic time. Less unplanned downtime, lower fuel and maintenance costs, and shorter servicing time are just some of the reasons why fleets are moving towards predictive maintenance.
PdM in the aviation industry
Predictive maintenance originated in the world of aviation when British scientist C.H. Waddington noted that “inspections tend to increase breakdowns” for the Royal Air Force Coastal Command 502 Squadron. Instead, he recommended a process that was more “in-tune with the actual condition of the equipment.”
PdM is still used by aviation companies to reduce the costly effects of maintenance-related flight delays and cancellations. These techniques and tools can also help airlines monitor engine health and performance during flights by measuring various temperature and vibration levels.
Getting started with predictive maintenance
How can organizations overcome the challenges of implementing PdM and quickly optimize their programs to see the full benefit of more proactive maintenance? Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing predictive maintenance.
- Identify assets to include in your PdM program
- Collect and log vital data
- Analyze the causes of failure and unplanned downtime
- Implement condition monitoring techniques and tools
- Develop algorithms for predicting failures
- Deploy to your pilot equipment
- Assess performance and scale your program across the organization
Want to see Limble in action? Get started for free today!
What’s next for predictive maintenance?
As technologies like IoT sensors continue to evolve and organizations further embrace big data, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and other next-generation tech, predictive maintenance strategies will grow more effective and more popular.
Whatever your organization’s objectives, whatever the maturity of your maintenance strategies, a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) can help you get a baseline understanding of your strengths and weaknesses and point the way to process improvement. Learn more about automation and analytics tools provided by cutting-edge CMMS tools in our Buyer’s Guide to these exciting solutions.
FAQ
Why use predictive maintenance software?
Predictive maintenance software streamlines processes, reduces errors and downtime, while enabling informed, data-driven decisions. It also helps with inventory management, lifespan of assets, and assists in meeting regulatory compliance, thereby enhancing overall productivity and profitability.
Table of Contents
- Predictive maintenance programs use technology to predict when equipment breakdowns will occur and prevent them.
- How does predictive maintenance work?
- Predictive maintenance challenges
- Benefits of predictive maintenance
- Predictive maintenance: industry use cases
- Getting started with predictive maintenance
- What’s next for predictive maintenance?
- FAQ
- Related Content
Predictive maintenance vs preventive maintenance
Preventive maintenance relies on usage and time intervals for maintenance schedules, while predictive maintenance uses condition sensors and algorithms. Predictive maintenance can be costly and challenging, thus not suitable for all assets. A blend of both strategies often yields success.
Table of Contents
- Predictive maintenance programs use technology to predict when equipment breakdowns will occur and prevent them.
- How does predictive maintenance work?
- Predictive maintenance challenges
- Benefits of predictive maintenance
- Predictive maintenance: industry use cases
- Getting started with predictive maintenance
- What’s next for predictive maintenance?
- FAQ
- Related Content
Is Limble Mobile CMMS app user friendly?
Limble is consistently rated Easiest-to-Use CMMS on review sites like G2, Capterra, and Software Advice. And our customers agree. With our mobile CMMS app, teams experience 30%+ better productivity, on average, requiring little to no training or ramp-up time. Our CMMS app can travel with your team, no matter where they go! Visit our App Store or Google Play for more information.
Table of Contents
- Predictive maintenance programs use technology to predict when equipment breakdowns will occur and prevent them.
- How does predictive maintenance work?
- Predictive maintenance challenges
- Benefits of predictive maintenance
- Predictive maintenance: industry use cases
- Getting started with predictive maintenance
- What’s next for predictive maintenance?
- FAQ
- Related Content
Can I connect to other systems?
Limble provides seamless, pre-built CMMS Integrations with the most widely used software systems. That means no help from a developer or your IT team is required. Learn more about our integrations.
Table of Contents
- Predictive maintenance programs use technology to predict when equipment breakdowns will occur and prevent them.
- How does predictive maintenance work?
- Predictive maintenance challenges
- Benefits of predictive maintenance
- Predictive maintenance: industry use cases
- Getting started with predictive maintenance
- What’s next for predictive maintenance?
- FAQ
- Related Content
How secure is the Limble CMMS platform?
At Limble, our world-class data security practices ensure your account information is safe. We use state-of-the-art technologies and industry best practices to maintain a secure infrastructure, including SOC-II Type II certification, regular penetration testing, and continuous security training for our staff.
Table of Contents
- Predictive maintenance programs use technology to predict when equipment breakdowns will occur and prevent them.
- How does predictive maintenance work?
- Predictive maintenance challenges
- Benefits of predictive maintenance
- Predictive maintenance: industry use cases
- Getting started with predictive maintenance
- What’s next for predictive maintenance?
- FAQ
- Related Content


